The Canadian food guide

The principles of this food guide are based on these foods:
- Dark green and one orange vegetable each day (broccoli, romaine lettuce, spinach, carrots, sweet potatoes and winter squash)
- Choose vegetables and fruit prepared with little or no added fat, sugar or salt.
- Enjoy vegetables steamed, baked or stir-fried instead of deep-fried.
- Have vegetables and fruit more often than juice.
- Eat a variety of whole grains such as barley, brown rice, oats, quinoa and wild rice.
- Enjoy whole grain breads, oatmeal or whole wheat pasta.
- Choose grain products that are lower in fat, sugar or salt.
- Drink skim, 1%, or 2% milk each day.
- Have meat alternatives such as beans, lentils and tofu often.
- Eat at least two Food Guide Servings of fish each week (herring, mackerel, salmon, sardines and trout).
- Trim the visible fat from meats. Remove the skin on poultry.
- Use vegetable oils such as canola, olive and soybean.
- Limit butter, hard margarine, lard and shortening.
- You can read more here
Mediterranean Pyramid
The Mediterranean diet plan includes these aliment groups:

- Cereals: bread and pasta, rice, maize, oats, luff, grain, potatoes.
- Beans, peas, lupins.
- Fruits: apples, pears, oranges, Mandarin, apricots, peaches, grape, fichi, water-melons, melons, raspberries, strawberries, chestnuts, walnuts, nuts, almonds, pistachio nuts.
- Vegetables: turnips, carrots, salads, spinach, broccoli, cabbages, tomatoes, eggplants, capsicum, zucchini, onions.
- Olive oil
- Aromatic grass: basil, thymus, oregano, garlic.
- Milk and cheeses
- Wine
The Latin America diet pyramid

Common Foods of the Latin American Diet
- Beans, Grains, Tubers, Nuts – Maize, Potatoes, Rice, Bread, Taro, Tortillas, Arepas, Black Beans, Seeds, Quinoa, Malanga, Peanuts, Amaranth, Legumes, Cassava, Pecans, Sweet Potatoes, Pumpkin, Plantains, Yuca, Garbanzo Beans, Pinto Beans
- Fruits – Limes, Bananas, Avocados, Cacao, Breadfruit, Plums, Apples, Berries, Papayas, Mangos, Cherimoya, Guanabana, Pineapple, Melon, Tamarind, Quince, Grapes, Guava, Oranges, Kiwi
- Vegetables – Kale, Cactus, Eggplant, Turnip, Chard, Squash, Zucchini, Onions, Broccoli, Okra, Spinach, Lettuce, Tomatoes, Tomatillos, Sweet Peppers, Chiles,
- Plant Oils and Milk Products – Plant Oils (Soy, Corn, Olive), Milk, Cheese
- Fish, Shellfish – Shrimp, Salmon, Snapper, Mussels
- Poultry & Pork – Fowl, Turkey, Chicken
- Meat, Sweets, Eggs
The Asian diet pyramid

Common Foods of the Asian Diet
- Fruits – Pineapple, Bananas, Mangos, Tangerines, Watermelon, Grapes, Pears
- Vegetables – Carrots, Broccoli, Mushrooms, Bok Choy, Cabbage, Bamboo Shoots, Chilis, Bean Sprouts, Scallions, Leafy Greens, Peppers
- Pasta – Rice (provides 25 to 80 percent of the calories in the daily diet), Noodles, Breads, Millet
- Beans – Soybeans, Peanuts, Dried Beans, Edamame Beans, Miso, Tofu
- Miscellaneous – Vegetable Oils, Fish/Shellfish, Egg, Poultry & Pork, Red Meat
- Sweets – Ice cream, Sorbets
The Vegetarian diet pyramid

Common Foods of the Vegetarian Diet
- Breads, Pasta & Grains – Oats, Wheat, Rice, Buckwheat, Flax, Bulgur, Quinoa, Amaranth, Seitan, Millet, Barley, Whole Grain Bread, Rye, Pita, Tortilla, Rice Cakes, Couscous, Noodles, Kasha, Pasta, Corn
- Fruits – Grapes, Raisins, Pears, Avocados, Oranges, Melon, Apples, Bananas, Plums, Cherries
- Vegetables – Mushrooms, Tomatoes, Kale, Broccoli, Collards, Sweet Potatoes, Peppers, Asparagus, Cucumber, Potatoes, Onions, Carrots, Cabbage, Squash, Leeks, Eggplant, Celery, Lettuce, Legumes & Beans: Soy, Red Bean, Lentil, Kidney Bean, Tempeh, Tofu, Black-Eyed Pea, Dried Pea, Soy Flour, Textured Vegetable Protein, Navy Bean, Miso, Pinto Bean, Split Pea, Lima Bean, Chick Pea, Black Bean
- Eggs
- Soy Milk, Cheese, Yogurt
- Nuts, Seeds – Pine, Walnut, Pistachio, Brazil, Pecan, Almond, Sesame, Cashew, Pumpkin, Hazelnut, Macadamia, Peanuts, Peanut Butter, Almonds, Pistachios, Pine Nuts, Walnuts, Pumpkin Seeds, Sesame Seeds
- Plant, Oils – Corn, Canola, Avocado, Olive, Soybean, Safflower, Peanut
- Sweets – Pie, Custard, Ice Cream, Cake, Cookies
The eatwise pyramid

The EatWise Pyramid is a visual guide to healthful living based on the Mediterranean Diet Pyramid. It emphasizes such things as eating a balanced diet, drinking plenty of water, getting regular physical activity, and drinking alcohol in moderation on a daily basis.
The EatWise pyramid was created by nutritionists from Harvard School of Public Health and Oldways Preservation Trust in January 2003 as an alternative to the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) food guide pyramid (See below), which the USDA has since replaced with MyPyramid (See below).
My Pyramid

MyPyramid, released by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) on April 19, 2005, is an update on the ubiquitous U.S. food guide pyramid (See below).
MyPyramid contains eight divisions. From left to right on the pyramid are six food groups:
- Grains, recommending that at least half of grains consumed be as whole grains
- Vegetables, emphasizing dark green vegetables, orange vegetables, and dry beans and peas
- Fruits, emphasizing variety and de emphasizing fruit juices
- Oils, recommending fish, nut, and vegetables sources
- Milk, a category that includes other dairy products
- Meat and beans, emphasizing low-fat and lean meats such as fish as well as more beans, peas, nuts, and seeds
The Food guide pyramid
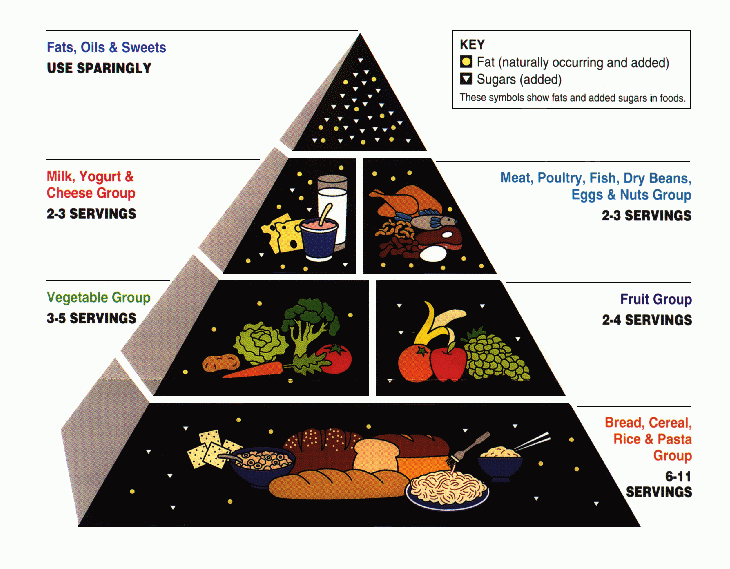
The improved American food guide pyramid was a nutrition guide created by the USDA. Released in 1992. On April 19, 2005, the USDA released the food guide pyramid’s successor, MyPyramid.
In general terms, the food guide pyramid recommends the following intake of different food groups each day.
- 3-5 servings a day of vegetables, especially dark green vegetables and orange vegetables.
- 2-4 servings of fruit a day are required, especially fresh and frozen fruits.
- 2-3 servings of meat, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, or nuts a day, especially dry bean and peas, eggs, and nut and seeds.
- 2-3 servings of milk, cheese, yogurt or milk substitutes a day.
- Occasional use of fats, oils, and sweets, especially oils.
- 6-11 servings of grains a day, especially whole grains.
The Native american food pyramid

The diets of the American Indians varied with the locality and climate but all were based on animal foods of every type and description, not only large game like deer, buffalo, wild sheep and goat, antelope, moose, elk, caribou, bear and peccary, but also small animals such as beaver, rabbit, squirrel, skunk, muskrat and raccoon; reptiles including snakes, lizards, turtles, and alligators; fish and shellfish; wild birds including ducks and geese; sea mammals (for Indians living in coastal areas); insects including locust, spiders and lice; and dogs. (Wolves and coyotes were avoided because of religious taboos). More…
The healthy diet Pyramid

The Healthy Diet Pyramid is a guide, to help you plan and eat a well balanced diet each day.
In general, you should select more food from the base of the pyramid (the carbohydrates), and less from the top of the pyramid (fats, oils, sugar, salt).
- Rice and alternatives – Placed at the base of the Pyramid are rice, noodles, bread, pasta, cereals, porridge, lontong, chapati, naan, idli, thosai & biscuits. These foods are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates, vitamins & minerals & dietary fibre. You should consume at least five servings daily, preferably including one serving of wholegrain products.
- Fruit – This group consists of fresh, dried, frozen, canned fruit and fruit juices. They are rich sources of vitamin A, C, potassium, fibre (excluding fruit juices) and flavonoids. Take two servings a day, especially the deeply or brightly (yellow, orange) coloured ones.
- Vegetables – This group consists of leafy, non-leafy, cruciferous and root vegetables. They are rich sources of vitamins A, C, folic acid, minerals such as calcium, iron, potassium, fibre and phytochemicals. Take two servings a day and include one serving daily of dark green or yellow-orange vegetables.
- Meat and alternatives – This group includes meat, poultry, fish, seafood, milk, milk products, nuts and seeds. These foods are excellent sources of protein, calcium, B-vitamins, iron and zinc. Take at least two servings a day.
The Pyramid of Singaporeans

- The small tip of the Pyramid shows fats, oils, sugar and salt. These are foods such cooking oils, butter, margarine, sugars, sweet desserts, seasonings and sauces.
- On the next level of the Healthy Diet Pyramid are foods that come mostly from animals: Meat and Alternatives like beef, lamb, mutton, pork, poultry, fish, dry beans, eggs, milk, yogurt, cheese; nuts and seeds. These foods are for protein, calcium, iron, and zinc.
- The third level includes foods that come from plants – Vegetables and Fruits. Most people need to eat more of these foods for the vitamins, minerals, and fibre they supply.
- At the base of the Healthy Diet Pyramid are Rice and Alternatives like noodles, breads, cereals, chapati, and pasta – all foods from grains. Your daily meals should include largest number of servings of these foods each day.
The Okinawa diet food pyramid

The Okinawa Dietâ„¢ Food Pyramid is based upon the traditional dietary habits of Okinawan elders, who have been proven to have the healthiest diet in the world.
The Okinawa-Diet food guide pyramid emphasizes eating healthy fat, calcium, flavonoid and omega-3 rich foods. Whole grains and other “Right Carbs” along with vegetables make up the base of the pyramid.
In base of a definition from “Your dictionary” – A diet pyramid is: A graphic representation of the structure of a food chain. And a diagrammatic representation of recommended portions of basic food groups.
From a review of the Mayoclinic – The basic principles of all food pyramids are largely the same and generally emphasize the following:
- Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
- Reduce intake of saturated fat, trans fat and cholesterol.
- Limit sweets and salt.
- Drink alcoholic beverages in moderation, if at all.
- Control portion sizes and the total number of calories you consume.
- Include physical activity in your daily routine.
- Eating a variety of foods within each group


